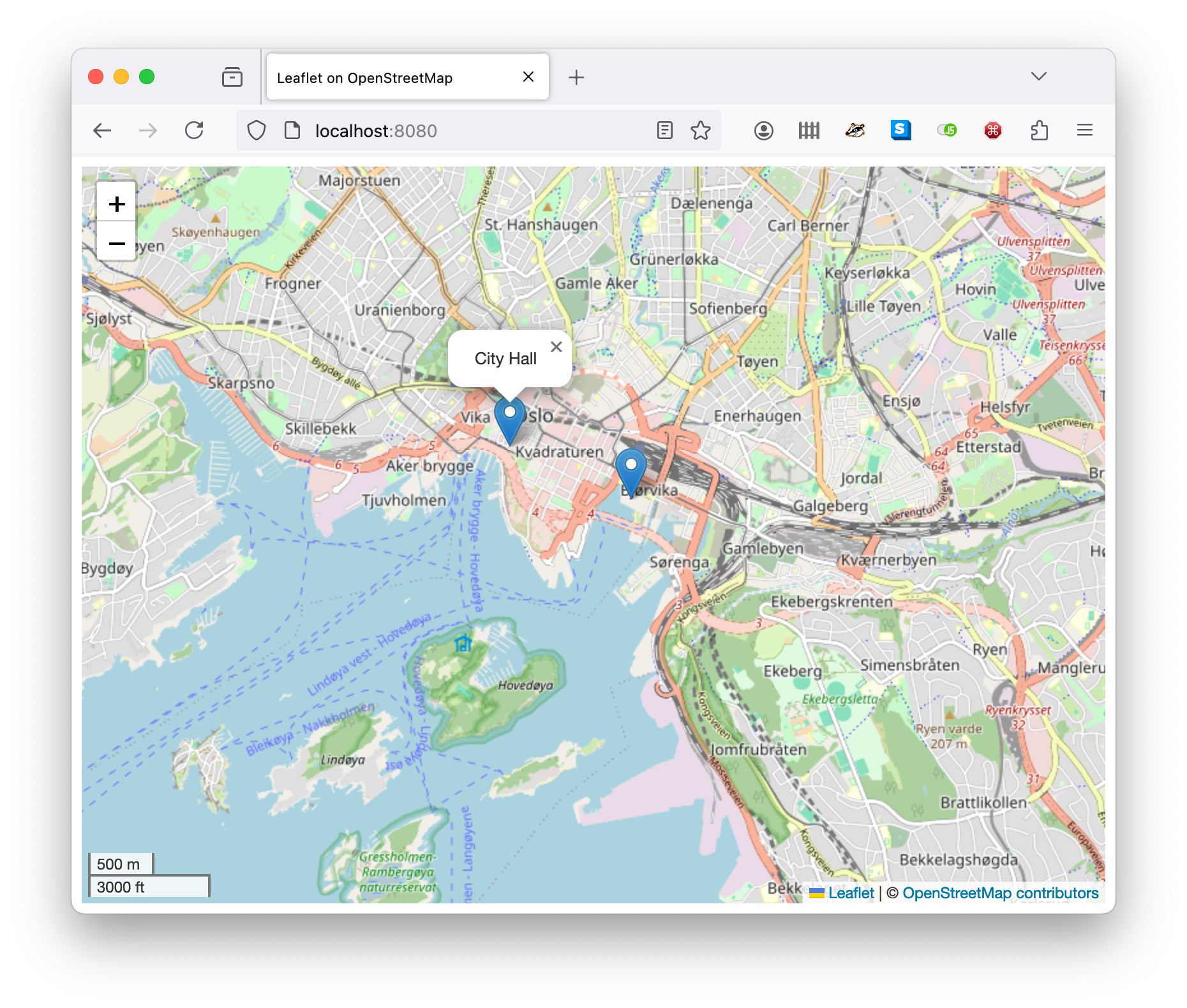
Displaying geo-annotated information
The Model API of ABS lets us display information in various ways. This example shows how to display geo-annotated ABS data on a map. To display the map in a browser, we use OpenStreetmap via the Leaflet library.
The complete code for this example can be found at https://github.com/abstools/absexamples/tree/master/collaboratory/examples/gis-modeling/.
Coordinates in ABS
In OpenStreetmap, coordinates are given as a (lat, long) pair of
floating-point numbers. We model map data as MapData(Float lat, Float long, String description), which is then returned via the Model
API. The complete code of the ABS part is as follows:
module MapObjects;
data MapData = MapData(Float lat, Float long, String description);
interface OMap {
[HTTPCallable] Pair<Float, Float> getInitialCoordinates();
[HTTPCallable] List<MapData> getMapObjects();
}
class OMap implements OMap {
Pair<Float, Float> getInitialCoordinates() {
return Pair(59.90, 10.73);
}
List<MapData> getMapObjects() {
return list[MapData(59.91115, 10.7357, "City Hall"),
MapData(59.90758, 10.75197, "Opera House")];
}
}
{
[HTTPName: "map"] OMap m = new OMap();
}Accessing and displaying coordinates
When the running model is accessed via a browser, the createMap
function in the model’s
index.html
file is called. This function creates a map, sets its initial
location according to the getInitialCoordinates method (Lines 6-12), then adds
the objects returned by the getMapObjects method (Lines 14-17). Both of these ABS
methods are called from JavaScript code in createMap (Lines 2, 3).
|
|
Running the Example
Since the model includes a custom html page and support library, the
compiler needs to run with the --modelapi-index-file and
--modelapi-static-dir arguments. See the
Makefile
for the commands to compile and run the example on the Erlang or Java backend.
After starting the model, the map can be accessed at
http://localhost:8080.